A guardrail is a safety barrier system designed to safely contain and redirect errant vehicles away from roadside hazards. Guardrails typically comprise a steel beam supported by steel posts that are driven directly into the ground. As the guardrail beam deflects it absorbs the energy of the impacting vehicle preventing serious injury or harm to motorists.
What is a Guardrail?
Types of Guardrails
The classification of guardrails considers the deflection (movement) of the system during a vehicle collision and the type of hazard to be shielded.
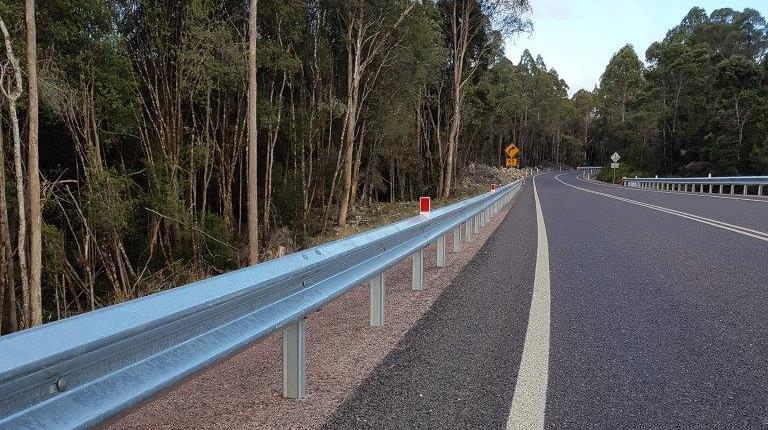
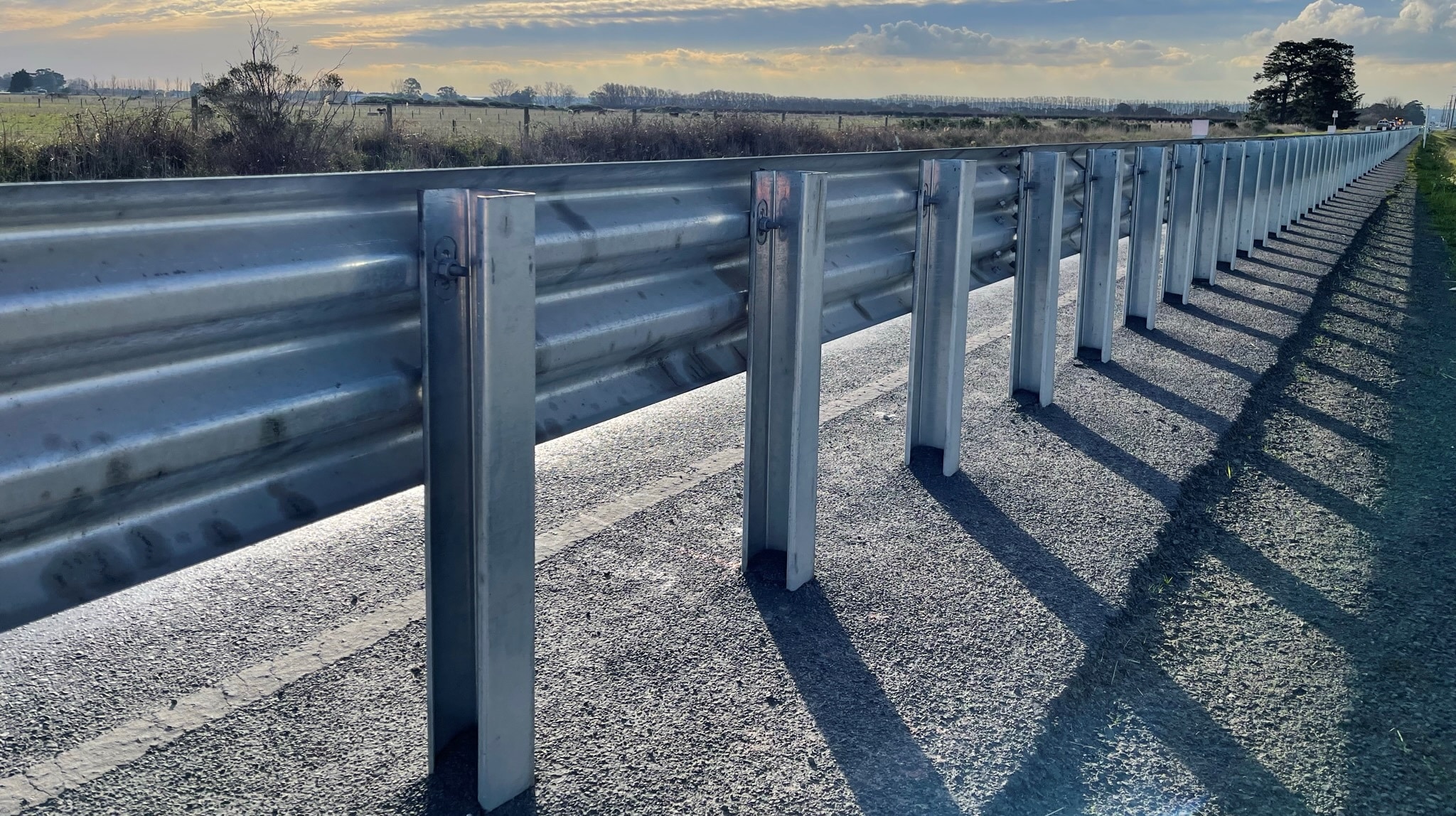
1. Flexible Guardrail Systems
Designed for roadway applications and feature w-beam guardrails supported by lightweight steel posts. The larger dynamic deflection of these crash barriers during a vehicle collision maintains vehicle stability and reduces occupant risk.
- W-beam guardrails supported by lightweight posts.
- Safe vehicle containment and redirection.
- Compliant to MASH and AS/NZS 3845: 2015.
- Low occupant ride down decelerations.
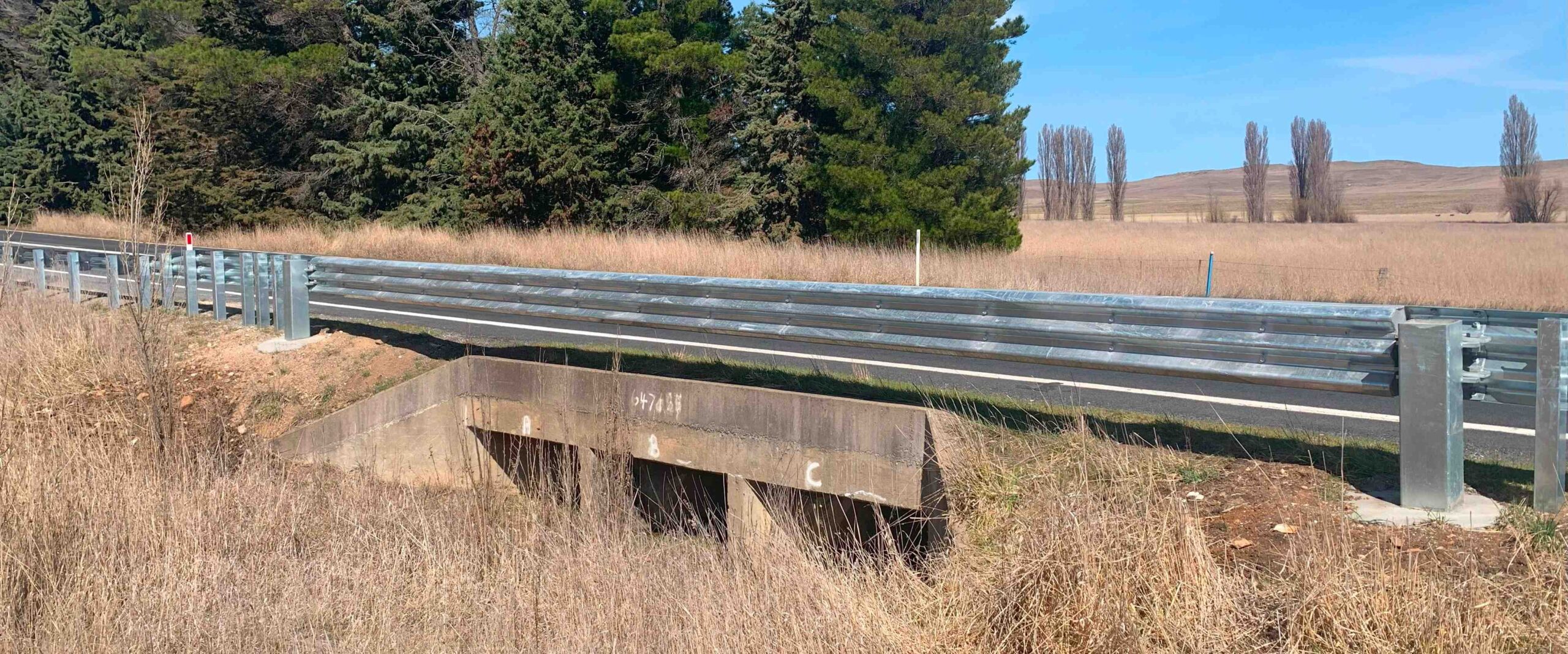
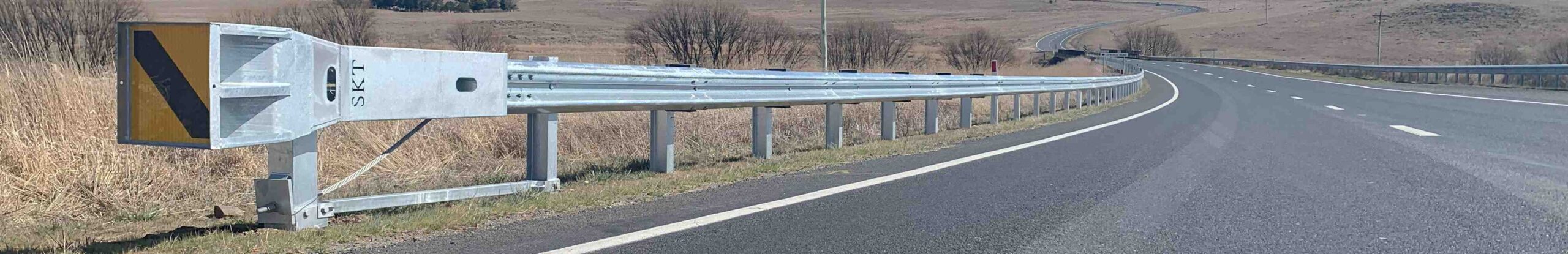
2. Semi-Rigid Guardrail Systems
Designed for roadway applications and feature either w-beam or thrie-beam guardrails supported by strong steel posts. The strength of the posts increases lateral resistance of the crash barrier system during a vehicle collision, limiting dynamic deflection and shielding hazards within close proximity to the roadway.
- W-beam or thrie-beam guardrails supported by strong posts.
- Strength of the system limits dynamic deflection.
- Compliant to MASH and AS/NZS 3845: 2015.
- Shields hazards within close proximity to the roadway.
3. Cable Guardrail Systems
Cable barriers also known as wire rope safety barriers rely upon the tensile strength of wire cable to contain and redirect an errant vehicle. The large deflection maintains vehicle stability and reduces occupant risk.
- Tensioned wire rope cables supported by steel posts.
- Stable vehicle containment and redirection.
- Compliant to MASH and AS/NZS 3845: 2015.
- Posts installed in concrete sockets to facilitate ease of repair.
4. Pedestrian Guardrails
Pedestrian guardrails are often installed along footpaths near schools or urban areas and are designed to channel pedestrians to safe crossing locations. Their robust design creates confidence for nearby pedestrians.
- Restricts pedestrians from entering the roadway at unsafe locations.
- Features robust steel vertical balusters.
- May be powder coated to match the urban environment.
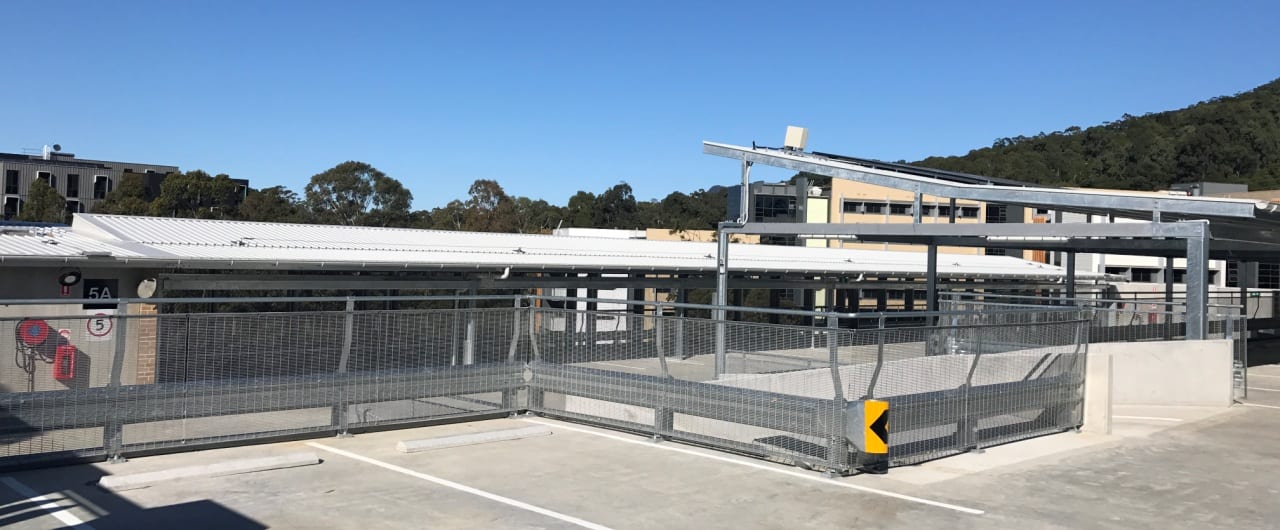
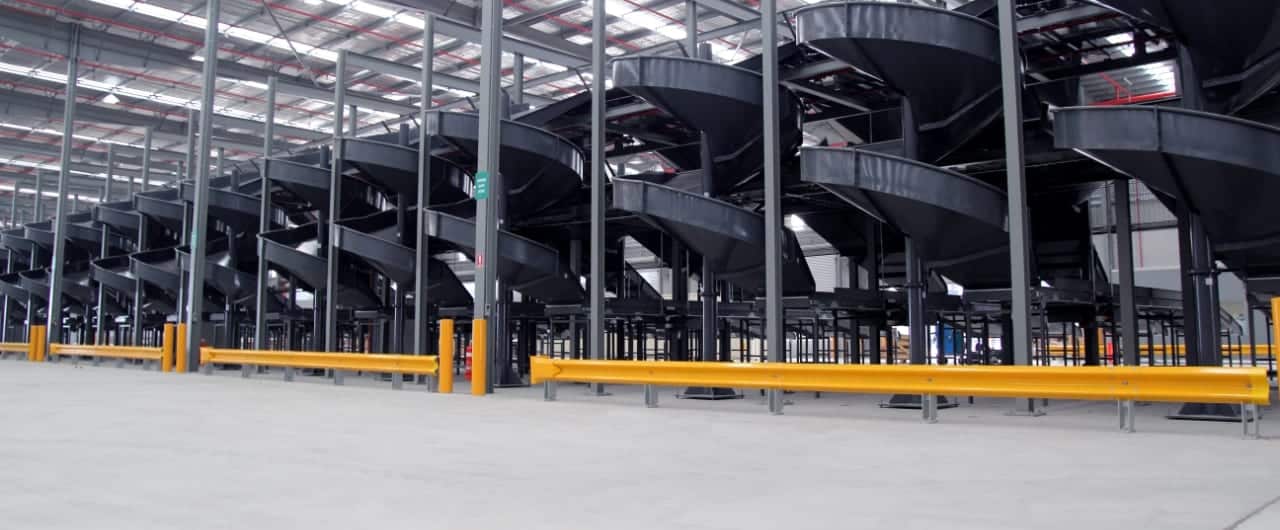
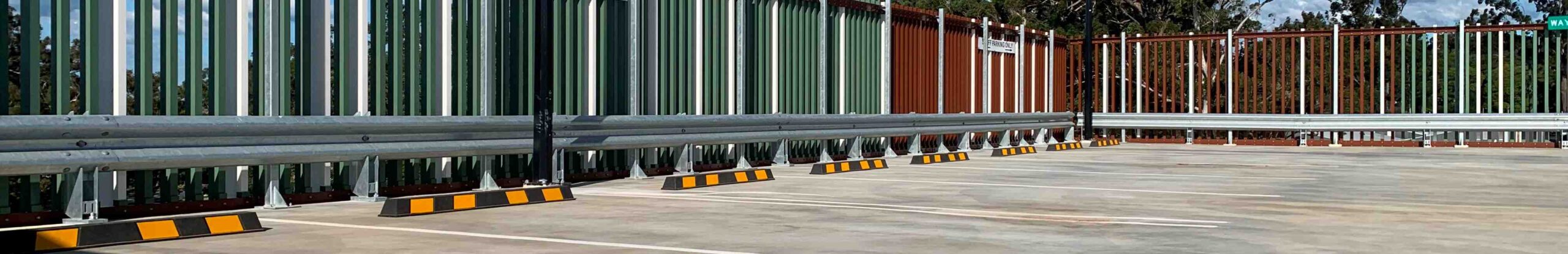
5. Car Park & Industrial Guardrails
Car park & industrial guardrails typically feature posts with base plates secured to a concrete foundation. There are designed to shield a drop to a lower level or restrict the passage of vehicles. Many car park & industrial guardrails designs consider pedestrians and feature handrails or fall protection panels.
- Designed to protect people, plant and equipment.
- Safe containment of low-speed vehicle impacts.
- Compliant to the vehicle impact loads described in AS/NZS 1170.1: 2002.
Guardrail Materials & Specifications
Installation & Maintenance
Guardrails must be installed in accordance with manufacturers specifications. The installation process typically comprises the following:
- Site establishment including investigation of underground services and provision of traffic control.
- Installation of posts by either driving directly into the ground or bolting to a concrete foundation.
- Attachment of the guardrail beam and securing with fasteners.
- Inspection of the assembly as per manufacturer guidelines.
Regular inspection and maintenance of the guardrail barrier system is recommended.
- Damaged items are replaced.
- There is no debris around the system that may impede the barrier.
- The system is appropriate delineated.
- The system has not been modified.
Australian Compliance
Guardrail barriers used for roadway applications should be reviewed and accepted by the Austroads National Safety Barrier Assessment Panel (ASBAP) which assesses the crashworthiness and suitability of road safety barriers, systems and devices for deployment on roads managed by Australian/New Zealand transport agencies. Products submitted to ASBAP must demonstrate compliance with the following guidelines:
- The Manual for Assessing Safety Hardware (MASH)
- AS/NZS 3845:2015 Road Safety Barrier Systems
Frequently Asked Questions
How do I choose the right guardrail system for my project?
The selection of a guardrail system should consider the location of the barrier, vehicle impact conditions and compliance requirements. A roadside guardrail is designed for high-speed vehicle impacts whilst a pedestrian or car park guardrail is designed for low-speed, nuisance impacts.
What is a compliant guardrail?
A guardrail system should be crash tested to demonstrate compliance with Australian Standards. Crash testing evaluates barrier performance and occupant risk.
What is the purpose of a guardrail?
A guardrail is designed to shield hazards and safely contain and redirect an errant vehicle. Guardrails are typically installed along roadways to prevent serious run-off-the-road accidents.
How are guardrails manufactured?
Guardrails are manufactured from steel and are classified as either w-beam or thrie-beam. Most guardrails are roll-formed and hot dip galvanised providing a durable finish.